Reference : chord
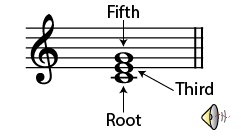
Three or more notes played at the same time form a chord. Traditionally, chords are formed by superimposing two or more thirds. For example, the notes C-E-G form a chord, or major triad. The note on which the chord is based is called the root. The other notes are called by the name of the interval they form in relation to the root:
See C > Chords for related entries
